مقدمة عن المعايير الأساسية لشبكة الحافلات
تاريخ الإصدار: 2026-02-02
Table of Contents
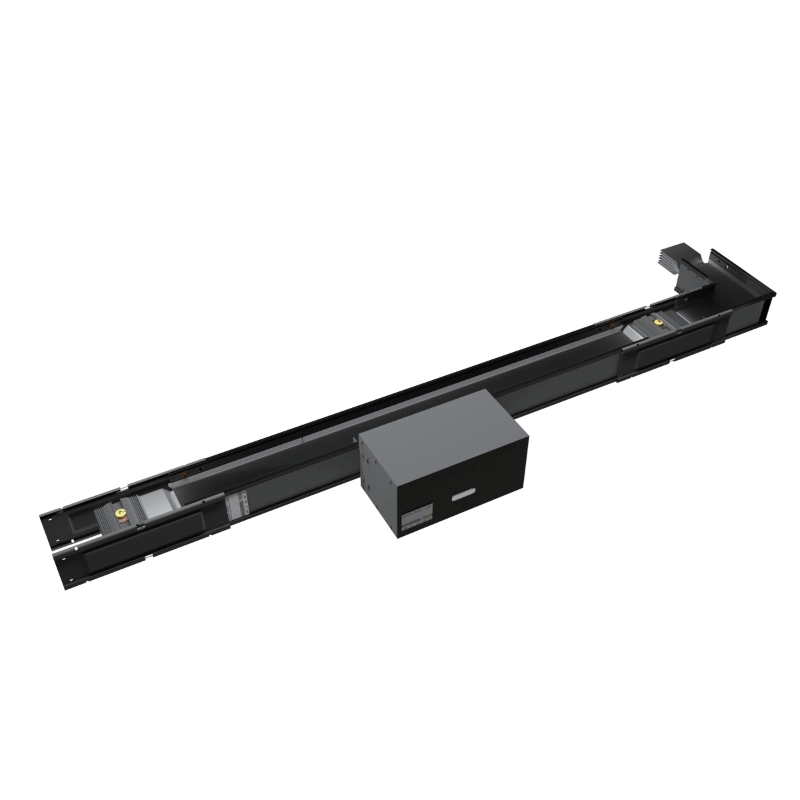
As a critical component in modern power transmission systems, Busways (also known as Bus Ducts or Busbar Trunking Systems) are widely applied in industrial plants, commercial buildings, and large venues. They efficiently transmit electrical energy from distribution centers to various load equipment. Busways are characterized by their compact structure, high transmission capacity, high safety standards, and ease of maintenance.
With the continuous development of the power industry, busway technology continues to innovate. Its performance is constantly improving, and its scope of application is expanding. Understanding the relevant knowledge of busways is essential for their correct selection and application.
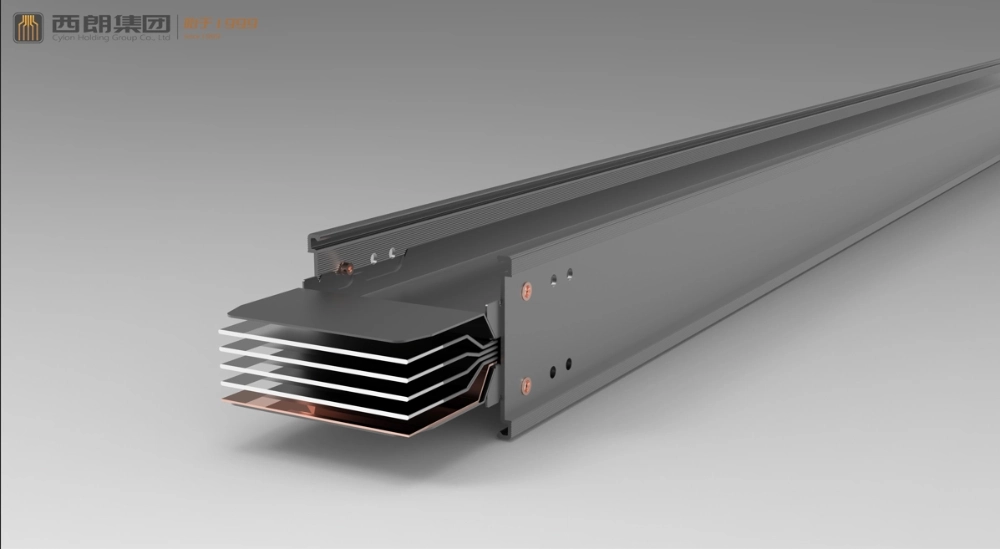

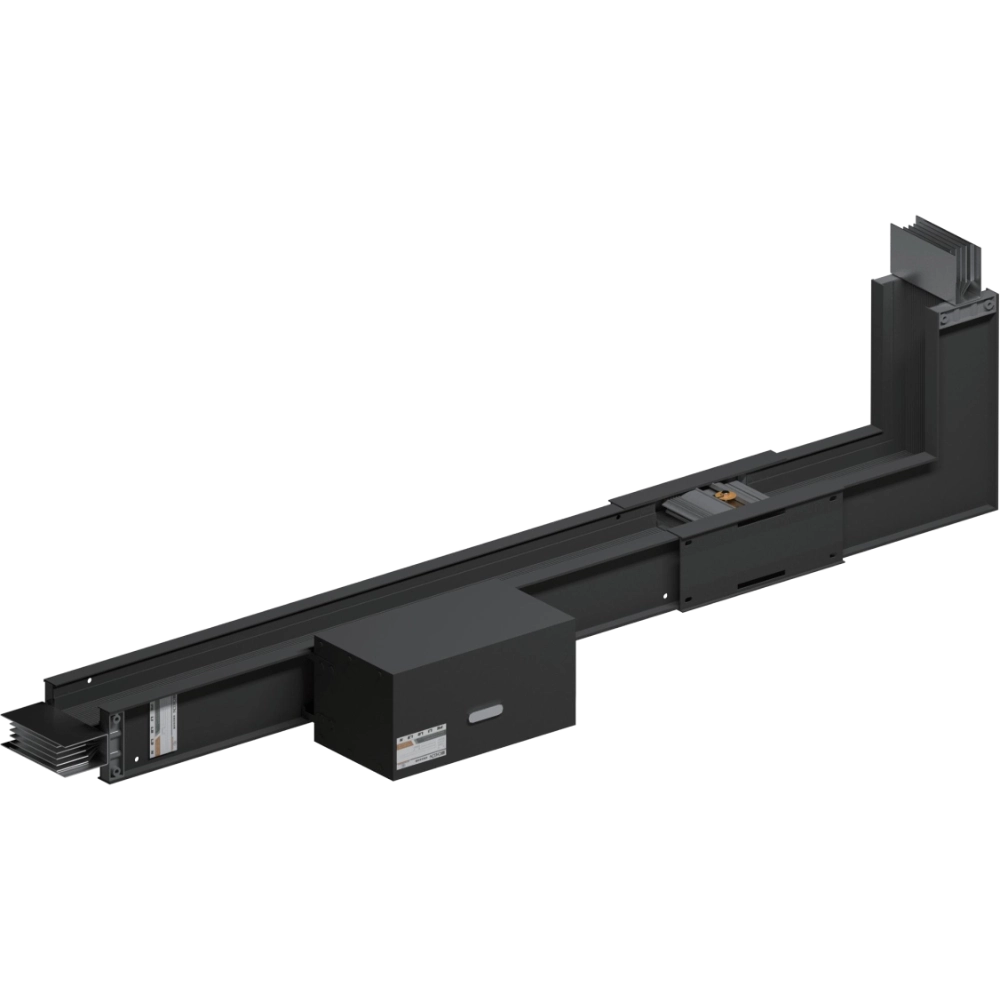
Basic Composition and Functions
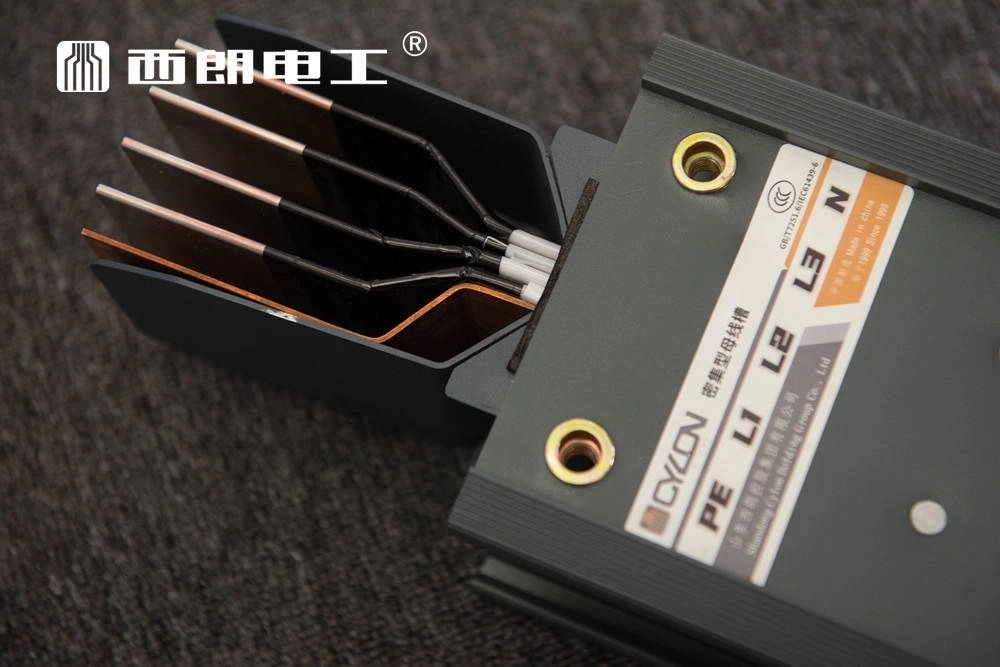
- Conductor: typically made of copper or aluminum, this is the core component of the busway responsible for power transmission. The cross-sectional area is determined based on the current carrying capacity (ampacity) requirements.
- Insulation Layer: This wraps around the conductor to provide electrical isolation, preventing short circuits between conductors or between a conductor and the enclosure. Common materials include epoxy resin and PVC.
- Enclosure (Housing): Generally made of metal materials such as steel plates or aluminum alloys, the enclosure protects the conductors and insulation layer. It also functions as a heat dissipator and provides mechanical support.
- Connecting Parts: These include connectors, flanges, and other components used to join busway sections, ensuring the continuity and reliability of power transmission.
Main Types and Applicable Scenarios
- Compact Busway (Dense-type): The conductors are arranged closely together (sandwich construction), resulting in excellent heat dissipation and high current carrying capacity. It is suitable for high-rise buildings, large shopping malls, and other locations with heavy electrical loads.
- Air-Insulated Busway: There are air gaps between the conductors. While the insulation performance is good and the cost is relatively lower, it is bulkier. It is suitable for general industrial plants, office buildings, etc.
- Fire-Resistant Busway: Possessing specific fire-resistance properties, this type can maintain normal operation for a certain period during a fire. It is suitable for hospitals, subways, and other locations with high safety requirements.
- Waterproof Busway: With excellent water resistance, this type can be used in humid environments or areas prone to water accumulation, such as underground garages and sewage treatment plants.
Comparison Advantages Over Traditional Cables
- High Current Carrying Capacity: The conductor cross-section of a busway can be made significantly larger, allowing for the transmission of higher currents to meet the needs of large equipment.
- Convenient Installation: Busways adopt a modular design. Installation simply involves connecting sections together. Compared to cable laying, this is much simpler and faster, significantly shortening the construction period.
- Easy Maintenance: The structure of a busway is simple, making faults easy to detect and repair. In contrast, cables are often buried underground or inside walls, making maintenance difficult.
- High Safety: The busway enclosure provides excellent protection, effectively preventing electric shock accidents. Conversely, cable insulation layers are prone to aging and damage, presenting potential safety hazards.

Installation Precautions
- Pre-Installation Check: Before installation, verify that the busway model and specifications meet the design requirements. Ensure the appearance is undamaged and all accessories are complete.
- During Installation: Maintain the busway in a horizontal or vertical position to avoid twisting or deformation. The spacing of brackets/supports must comply with standard regulations to ensure a secure installation.
- Connections: Connections between busways must be tight and reliable, and contact resistance must meet requirements. After connection, an insulation test should be conducted to ensure good insulation performance.
- Post-Installation: After installation is complete, clean any debris from inside the busway and check that all components are properly installed. Then, conduct a power-on trial run to observe if the operation is normal.
Conclusion
Busways offer significant advantages in power transmission. They feature a rational composition, diverse types, and a wide range of applicable scenarios. Compared to traditional cables, they are more competitive in terms of current carrying capacity, installation, maintenance, and safety. Strictly adhering to installation precautions ensures their normal operation. As technology progresses, busways will play an increasingly important role in power systems, providing a reliable guarantee for electricity usage in various facilities.